Pubblicato su ApJ “Investigating the Structure of Vela X” di P. Slane (CfA) sulla struttura del resto di supernova della Vela
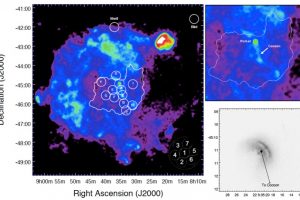
Le esplosioni di supernova, gli eventi più violenti dell’Universo, producono una nebulosa in rapida espansione che eventualmente interagisce con il mezzo interstellare circostante (chiamate “resti di supernova”) ed un oggetto compatto formatosi dalla contrazione del nucleo della stella progenitrice. Data la sua vicinanza dal Sole (“appena” 945 anni luce circa), uno dei resti di supernova più studiati e’ quello della
» Read more