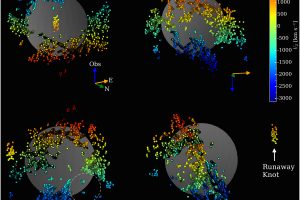
Emissione di raggi γ dai resti di supernova nella Grande Nube di Magellano. L’articolo: “High-energy γ-ray detection of supernova remnants in the Large Magellanic Cloud” di R. Campana (INAF – OAS) pubblicato su MNRAS
I resti di supernova sono nebulose in espansione prodotte dall’esplosione di stelle di grande massa. Sono oggetti di grande interesse astronomico per i vari processi fisici in atto in queste nebulose e perché permettono di comprendere diversi aspetti delle supernova e delle stelle massicce nelle fasi finali della loro evoluzione. In particolare, l’osservazione dei resti di supernova ai raggi γ
» Read more