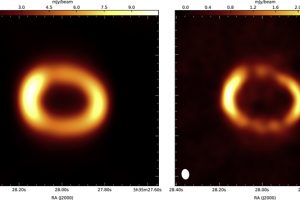
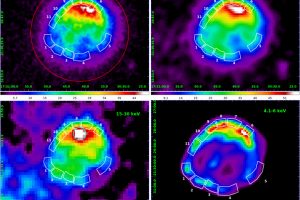
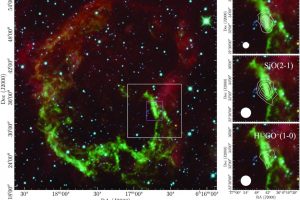
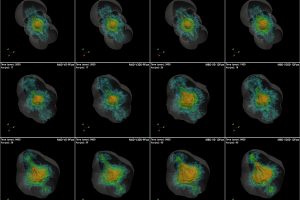
γ-ray emission from the supernova remnants in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The paper: “High-energy γ-ray detection of supernova remnants in the Large Magellanic Cloud” of R. Campana (INAF – OAS) recently appeared on MNRAS
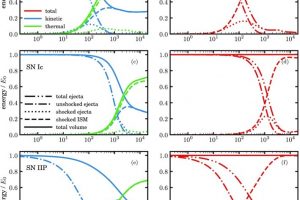
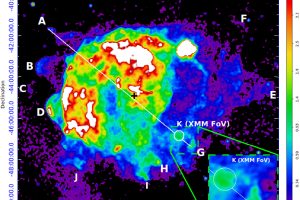
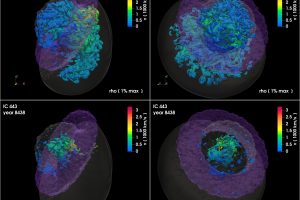
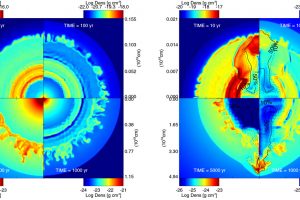
Supernova remnants are expanding nebulae produced by the explosion of high-mass stars. They are of great interest for understanding various physical processes and the final evolutionary stages of massive stars. Observations of supernova remnants in gamma rays are particularly important as they shed light on high-energy processes, such as the acceleration of cosmic rays (charged particles at very high energies).
» Read more