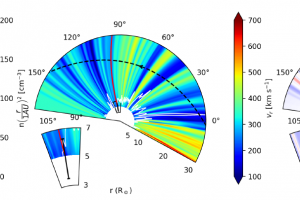
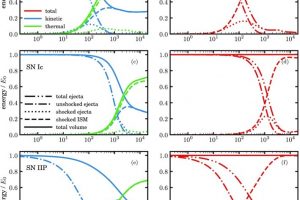
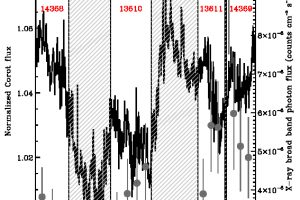
The magnetic field in SN1987A revealed from radio observations. The study: “Polarized radio emission unveils the structure of the pre-supernova circumstellar magnetic field and the radio emission in SN1987A” of O. Petruk (INAF-OAPA) appeared on A&A
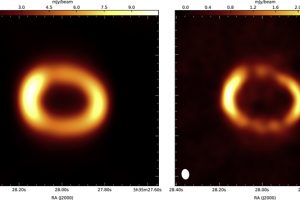
Without any doubts, the supernova remnants SN1987A is the one that taught us more about this class of objects and supernova exposions. Produced by a supernova exploded in the Large Magellanic Cloud on February 23rd 1987, this is the only case in which we have observations of the progenitor, of the supernova explosion, and in which we follow the development
» Read more