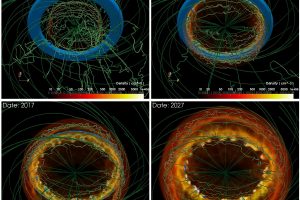
The supernova – supernova remnant connection in SN 1987A. The study: “Hydrodynamic simulations unravel the progenitor-supernova-remnant connection in SN 1987A” of S. Orlando (INAF-OAPA) recently appeared on A&A

Stars more massive than 9 solar masses end their evolution in spectacular supernova explosions. These explosions are triggered by the gravitational collapse of the core of such massive stars, once the thermonuclear reactions are exhausted and the core is not supported against gravity by the pressure produced by the reactions. Supernovae are not simple spherical explosions, but rather complex phenomena
» Read more