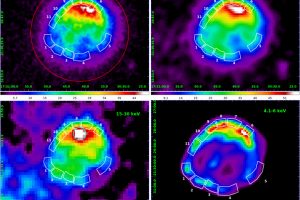
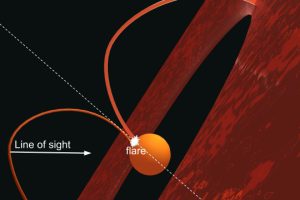
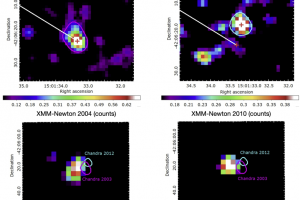
Superfast fragments and X-ray emission in the supernova remnant SN 1006. The study: “Indication of a fast ejecta fragment in the atomic cloud interacting with the southwestern limb of SN 1006” of R. Giuffrida (UNIPA/INAF) appeared on A&A
Supernova remnants, which are nebulae produced by explosion of supernovae and undergoing rapid expansion, typically serve as intense sources of high-energy radiation, particularly in the form of X-ray emissions. This radiation can be of two different types: thermal and non-thermal. Thermal radiation is emitted by dense material and is contingent upon the temperature of the emitting gas. To emit X-rays,
» Read more