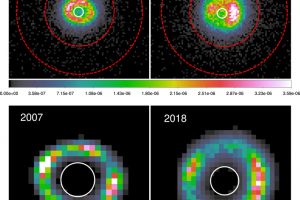
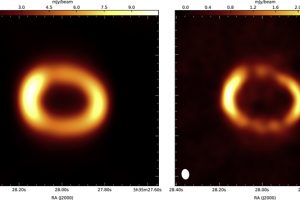
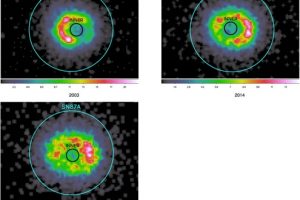
Simulated the XRISM observations of the iconic supernova remnant SN1987 A. The study: “Probing Shocked Ejecta in SN 1987A: A novel diagnostic approach using XRISM−Resolve” of V. Sapienza (UNIPA/OAPA) accepted on ApJL
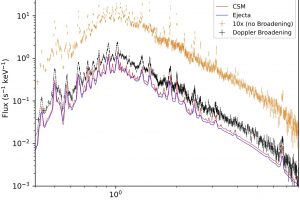
SN1987 A is one of the most significant objects for studying supernova explosions and their remnants. This is because it is the only core-collapse supernova that has occurred relatively close to us (approximately 170000 light-years away, in the Large Magellanic Cloud) in the modern epoch. Therefore, it is the sole object of this type for which we have telescope observations
» Read more