The role of the magnetic field during the evolution of supernova remnants i. The study: “Magneto-hydrodynamic simulations of young supernova remnants and their energy-conversion phase” of O. Petruk (IAPMM NASU) recently appeared on MNRAS
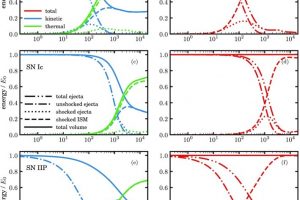
Supernova explosions are sorted into two categories: The thermonuclear explosions triggered by white dwarfs in close binary systems (type Ia) and those triggered by the gravitational collapse of the core of massive stars (type Ib/c and II). Because of the paucity of known supernova remnants younger than 1000 years, astronomers developed several models describing the evolution of supernova remnants to
» Read more

