Calendar
I will talk about two new possibilities to analyse the observational data on non-thermal emission of cosmic rays accelerated in supernova remnants (SNRs). The first one is related to the polarization images of SNRs. In fact, the polarized radio emission has been mapped with great detail in several Galactic supernova remnants, but has not yet been exploited to the extent it deserves. We have developed a method to model maps of the Stokes parameters for shell-like SNRs during their Sedov evolution phase. The second result bases on the time-dependent particle acceleration and relates the temporal evolution of the radio spectral index of SNR in the aftermath of the explosion to the gamma-ray spectrum at later stages. As a test case, we apply our method to describe gamma-rays from IC443; as a proxy of the IC443 parent supernova we consider SN1987A.
It is debated whether the long and intense flares observed on the PMS stars in Orion involve single and very long magnetic channels or much flatter loop arcades. This question is important because the long flaring channels may be so long as to connect the star to the circumstellar disk. In this work a new method solves the question …. (suspence is left on purpose).
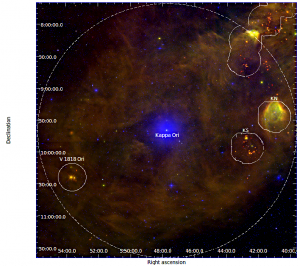
of young stellar objects around V1818 Ori. This is a follow up devoted to explore the eastern edge of a ring of dust around Kappa Ori(a B0 V star) that embeds groups of YSOs to the west of the star itself. My preliminary analysis shows that also the group of V1818 Ori belongs to the Kappa Ori cluster at 250 pc and is unrelated to the Mon R2 region to which it has been associated so far.
8 giugno ore 11.00 Seminario D. Coero Borga e S. Parisini La struttura di Comunicazione dell’INAF
Come sapete da maggio 2016 l’Inaf ha formalizzato una nuova struttura dedicata alla comunicazione. Com’è organizzata? Chi ci lavora? Cosa si intende per press release, news, conferenza stampa, embargo, comunicato congiunto, virgolettato e cose simili? A chi serve? E, soprattutto, perché parlano di qualunque cosa tranne che delle mie ricerche? Nel corso della prima parte di questo incontro, dedicata a tutti ma in particolare a ricercatrici e ricercatori (precari e non, dai laureandi agli associati già in pensione) tenteremo di soddisfare queste e altre curiosità e dubbi su due dei quattro compiti della struttura di comunicazione: ufficio stampa e Media Inaf. E di raccogliere i vostri suggerimenti. L’obiettivo è migliorare la comunicazione interna, riducendo al minimo i fraintendimenti e cercando di rendere il più possibile serene – magari perfino divertenti – le occasioni d’interazione con noi.
8 giugno ore 14.30 Seminario D. Coero Borga e S. Parisini Utilizzo di videocamera per la produzione di materiale multimediale
Il pomeriggio è dedicato ad una parte più tecnica – rivolta a chiunque ne abbia voglia ma in particolare a chi è interessato a produrre materiale multimediale (perlopiù video) per l’ufficio stampa, Media Inaf e Inaf-Tv – durate la quale daremo qualche rudimento sulle riprese video e faremo qualche simulazione d’intervista. Simulazioni che non verranno messe in rete, promesso: dunque massimo relax e nessun dress code.
Classical T Tauri stars are bright in the soft X-ray and far UV bands, because of large amounts of plasma at T~105-106 K, associated with the accretion-shock regions. Inspecting the emission from the shock region is important since it can potentially reveal fundamental properties of the accretion-stream material (i.e. geometry/density/velocity/abundances). However, the precise location of these hot plasmas (pre-shock? post-shock? different shock regions with different temperatures?) is still unclear. To constrain location and properties of these accretion-related hot plasmas, X-rays and UV observations are needed. The next XMM call (deadline 6 October 2017) offers the possibility to investigate this issue. I would like to discuss with you the opportunity to propose a joint XMM+HST program, focused on TW Hya, to perform time-resolved high-resolution spectroscopy on time scales down to 15 ks, simultaneously in the X-ray and UV bands. Correlated or uncorrelated variability of plasmas at 105 and 106 K will indicate whether or not they are located in the same accretion-shock regions. That will provide important constraints on the physical properties of the accretion streams in CTTS.
Abstract: For decades the Solar System has been our sole example of a planetary system, resulting in the classical view of planetary formation as a local, orderly process producing stable planetary systems. The ever growing sample of known exoplanets, however, has shown us the major role played by orbital migration and chaos in determining the evolution of planetary systems in our galaxy. This brought to questioning our very understanding of the history of the Solar System and to suggesting that it also could have undergone a more violent evolution than previously thought. In this talk I will describe how the compositional information on the planetary bodies of the Solar System can be used to shed new light on its past, illustrating the past and current investigations performed in the framework of the NASA missions Dawn and Juno, and I’ll discuss how the same principles, if not the same techniques, can be used to investigate of histories of extrasolar planets.
Abstract:
With significant new observing capabilities, centimeter-wavelength radio astronomy is currently in a renaissance leading up to the advent of the Square Kilometre Array (SKA). The sensitivity upgrades of both the NRAO Very Large Array (VLA) and the Very Long Baseline Array (VLBA) have begun to provide us with a much improved perspective on stellar centimeter radio emission, particularly concerning young stellar objects (YSOs) and ultracool dwarfs. For the first time we now have systematic access to the radio time domain. I will mainly present a deep VLA and VLBA radio survey of the Orion Nebula Cluster (ONC), where we have found hundreds of compact radio sources, a sevenfold increase over previous studies, and intricate detail on the radio emission of proplyds. We can now better disentangle thermal and nonthermal radio emission by assessing spectral indices, polarization, variability, and brightness temperatures (VLBA). With simultaneous radio-X-ray time domain information (Chandra), this project is providing first constraints on YSO radio flares and their relation with X-ray flares, as well as improved constraints on the overall high-energy irradiation of their surroundings, including protoplanetary disks. Starting with Orion, I will additionally discuss the use of the VLBA for precision stellar astrometry in the Gaia era, highlighting how VLBI astrometry is allowing us to extend the Gaia sample of YSOs and ultracool dwarfs by including embedded objects, distant obscured sources in the Galactic plane, and faint ultracool dwarfs, while providing important opportunities for astrometric cross-calibration.
