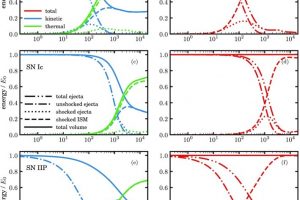
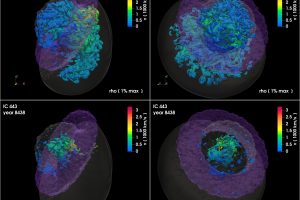
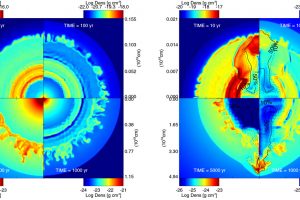
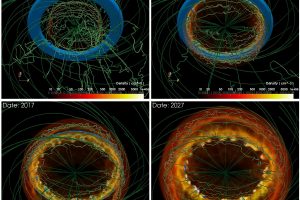
Supernova explosions produced by LBV stars. The study: “Modeling the remnants of core-collapse supernovae from luminous blue variable stars” of S. Ustamujic (INAF-OAPA) recently appeared on Astronomy & Astrophysics
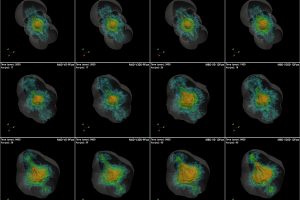
LBV (Luminous Blue Variable) stars are massive and unstable stars characterized by large mass-lost due to intense stellar winds and aperiodic bursts. Due to their instability, LBV stars are also variable, with quasi-periodic oscillations of their luminosity of the order of 0.5-2 magnitudes. Typical examples of this class of stars are: the supergiant S Doradus in the Large Magellanic Clouds,
» Read more