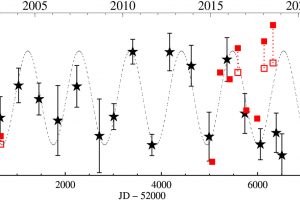
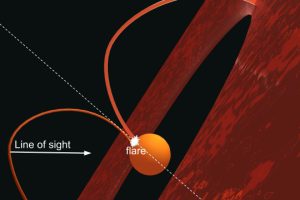
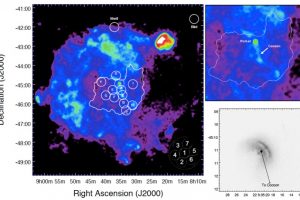
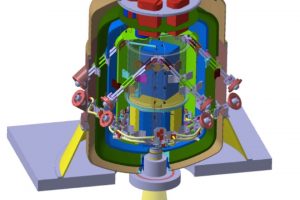
Simulazioni MHD dell’emissione radio da un arco magnetico in una T Tauri. L’articolo: “Predicting the time variation of radio emission from MHD simulations of a flaring T-Tauri star” di Waterfall C. O. G. (Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics) pubblicato su MNRAS
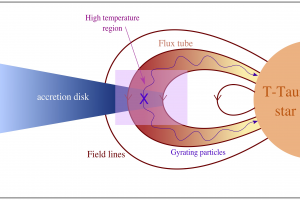
Le T Tauri sono stelle giovani (tipicamente più giovani di 5 milioni di anni), di piccola massa, circondate da un disco di polveri e gas chiamato disco protoplanetario. Il disco non raggiunge la superficie della stella attorno cui orbita: le polveri sublimano in prossimità della stella per le alte temperature raggiunte dal disco interno (oltre i 1500 gradi), mentre il disco di
» Read more