Prima misura diretta delle particelle relativistiche accelerate in onde d’urto nell’eliosfera descritta nello studio: “Direct Measurements of Synchrotron-emitting Electrons at Near-Sun Shocks” di I. C. Jebaraj (University of Turku)
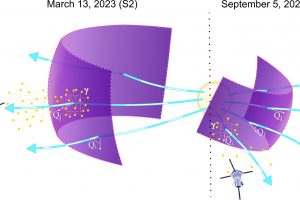
Nel cosmo esistono diversi ambienti caratterizzati da onde d’urto capaci di convertire l’energia cinetica di gas e flussi di particelle in calore, turbolenze, energia magnetica e, infine, di accelerare particelle fino a energie relativistiche, producendo raggi cosmici. Le dimensioni di tali sistemi possono variare di molti ordini di grandezza, dalle dimensioni tipiche dell’ambiente interplanetario fino agli enormi ammassi di galassie.
» Read more