Non thermal emission and cosmic rays in the supernova remnants SN1006. The paper: “”Hadronic particle acceleration in the supernova remnant SN 1006 as traced by Fermi-LAT observations” of M. Lemoine-Goumard (University of Bordeaux) appeared on A&A
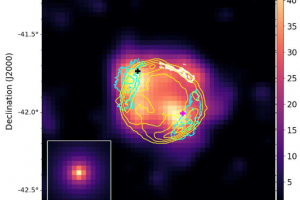
Supernova remnants serve as unique laboratories to understand the complex processes occurring during a supernova explosion and to investigate the internal structure of massive stars just before their explosive demise. Additionally, the study of these remnants is driven by their crucial role in accelerating cosmic rays, which are particles with extremely high energies. In 1949, Enrico Fermi laid the groundwork for
» Read more