Filaments in Cas A probe the processes occurred inside the progenitor during the explosion. The paper: “Filamentary ejecta network in Cassiopeia A reveals fingerprints of the supernova explosion mechanism” of S. Orlando (INAF-OAPA) appeared on A&A
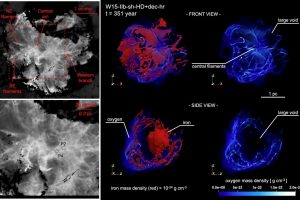
A new theoretical study shows that the filamentary structure observed in the supernova remnant Cassiopeia A (Cas A) is a direct consequence of the processes that occurred in the progenitor star immediately after core collapse. Supernovae are among the most energetic explosive events in the Universe. Yet, despite their immense brightness, they convert only about 1% of their energy
» Read more