The properties of the reverse shock in Cas A reveal properties of the progenitor. The paper: “Evidence for past interaction with an asymmetric circumstellar shell in the young SNR Cassiopeia A” of S. Orlando (INAF – OAPA) recently appeared on A&A
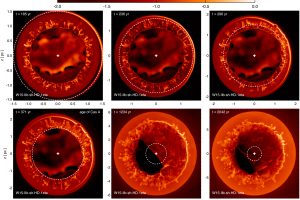
Supernova remnants (expanding clouds produced by the explosion of massive stars) are fascinating objects. Their study, in fact, can unveil the physical processes working during supernova explosions and even the properties of the stellar progenitors. To these aims, of particular importance is the analysis of the physical and chemical properties of the ejecta (which are the fragments of the dying
» Read more
