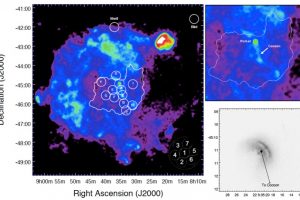
Jets launched during supernova explosions. The study: “X-ray emitting structures in the Vela SNR: ejecta anisotropies and progenitor stellar wind residuals” of V. Sapienza (UNIPA/OAPA) recently appeared on A&A
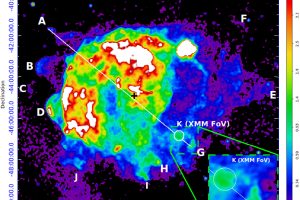
Supernova remnants are clouds in rapid expansion formed by supernova explosions. Typically, these remnants are very inhomogeneous. These inhomogeneity is the result of the interaction between the expanding remnant and the surrounding material, and, in particular when they are generated by core-collapse supernova explosions (which are the supernova triggered by the gravitational collapse of the cores of massive stars), also to anisotropies formed
» Read more