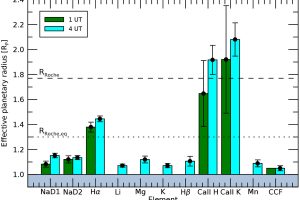
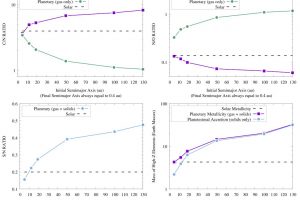
The properties of the exoplanets sculpted by the forming environment. The study: “Exploring the link between star and planet formation with Ariel” of D. Turrini (INAF-IAPS) appeared on Experimental Astronomy
To date (October 2021, data from https://exoplanets.nasa.gov/), astronomer discovered enough exoplanets (in excess of 4500) to allow not only analysis of individual planets, but also detailed studies of the whole exoplanets population. These studies are necessary to fully understand the process of planets formation, the evolution of planets, the chemical composition and physical properties of planets atmospheres, and how the forming
» Read more