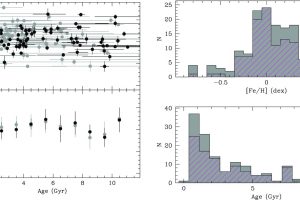
The magnetic activity vs. age in binary systems with a white dwarf and a main sequence star. The study: “Main-sequence companions to white dwarfs – II. The age-activity-rotation relation from a sample of Gaia common proper motion pairs” of A. Rebassa-Mansergas (Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya) recently appeared on MNRAS

Several stellar phenomena and evolutionary processes are connected to their magnetic fields. The mechanisms that allow stars to produce their magnetic fields depend on their internal structure and stellar properties. One dominant property is stellar rotation: the faster stars rotate, the more intense their magnetic field and magnetic activity. Since stellar rotation declines with age, it is not surprising that
» Read more