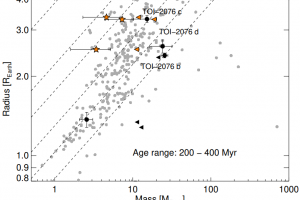
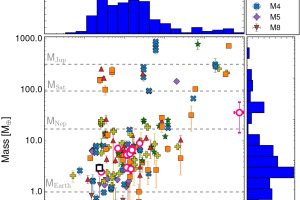
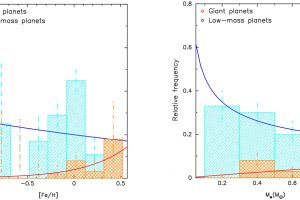
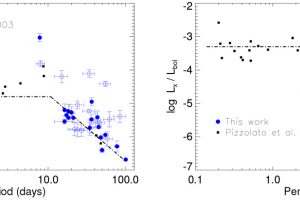
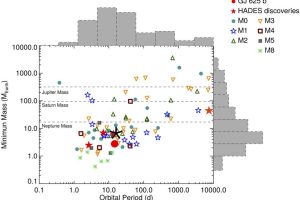
A young Saturnian planet orbiting a star in the stellar cluster IC 2602 described in the study: “TOI-837 b: Characterisation, formation, and evolutionary history of an infant warm Saturn-mass planet” of M. Damasso (INAF – OATo)

Analysis of TESS and HARPS observations confirms the existence of a Saturn-like planet orbiting a star associated with the young stellar cluster IC 2602 Stellar clusters are not only beautiful objects to photograph and observe through a telescope, but they also represent an important opportunity for studying stellar evolution. In fact, they are composed of rich samples of stars
» Read more