Different regimes of particle acceleration in supernova remnants. The study: “A Spatially Resolved Study of Hard X-Ray Emission in Kepler’s Supernova Remnant: Indications of Different Regimes of Particle Acceleration” of V. Sapienza (UNIPA/OAPA) appeared on ApJ
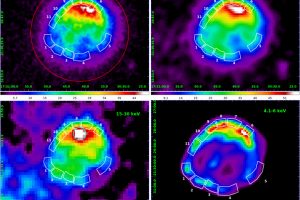
Cosmic rays are high-energy charged particles which continuously hit our planet. These particles are accelerated up to such high velocities in different astronomical environments, among which supernova remnants seems to be particularly important. These objects are nebulae in rapid expansion generated by the explosions of very massive stars. In supernova remnants, particle acceleration seems to occurr along the expanding shock
» Read more