Una nuova super-Terra scoperta con HARPS-N: Pubblicato su A&A lo studio: “HADES RV Programme with HARPS-N at TNG. V: A super-Earth on the inner edge of the habitable zone of the nearby M dwarf GJ 625” di A. Suárez Mascareño
di Mario Giuseppe Guarcello ( segui mguarce)
La famiglia degli esopianeti classificabili come super-Terre (pianeti rocciosi con massa tra 2 e 10 volte maggiore di quella della Terra), potenzialmente abitabili, si arricchisce di un nuovo membro.
La rivista Astronomy & Astrophysics ha recentemente pubblicato lo studio “HADES RV Programme with HARPS-N at TNG. V: A super-Earth on the inner edge of the habitable zone of the nearby M dwarf GJ 625” di A. Suárez Mascareño (Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias) riguardante l’identificazione di una nuova super-Terra orbitante attorno la stella GJ 625 (classe spettrale M) e distante appena 21.2 anni luce dal Sole. Il pianeta, con una massa di 2.8 masse terrestri, orbita con un periodo di 14.63 giorni ad una distanza di 0.078 UA (Unità Astronomiche, la distanza media tra Terra e Sole) dalla sua stella, ossia all’interno della fascia di abitabilità (la regione attorno una stella dove un pianeta può ospitare acqua allo stato liquido).
La scoperta ha richiesto l’analisi di 151 spettri ad alta risoluzione della stella raccolti in 3.5 anni con lo spettrografo HARPS-N, montanto al Telescopio Nazionale Galileo ed oggi una delle punte di diamante per la ricerca di esopianeti a disposizione della comunità scientifica internazionale. Il progetto ha coinvolto la comunità italiana di GAPS (Global Architecture of Planetary Systems), l’Institut de Ciències de l’Espai de Catalunya (ICE), e l’Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias (IAC), ed ha visto la partecipazione degli astronomi Laura Affer, Giuseppina Micela, Jesus Maldonado e Antonio Maggio.
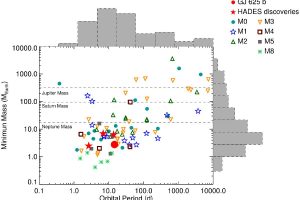
L’immagine in evidenza (link) mostra la distribuzione di massa vs. periodo orbitale dei pianeti noti orbitanti attorno stelle di tipo spettrale M.
